- 06
- Mar
Demystifying PCB Components: A Beginner’s Guide to Electronic Circuits
Introduction:
Are you fascinated by the inner workings of electronic devices? Do you find yourself curious about the tiny components that make them tick? Welcome to the exciting world of printed circuit boards (PCBs), where every component plays a crucial role in bringing your gadgets to life.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll take you on a journey through 12 commonly used components found on PCBs. Whether you’re a beginner or have dabbled in electronics before, understanding these basics is key to unlocking the mysteries of circuitry.
Understanding PCB Components: Imagine a printed circuit board (PCB) as the backbone of your electronic gadgets—a dynamic puzzle board that connects and supports various electronic components. At first glance, deciphering the components on a PCB may seem daunting. Fear not! We’re here to break down 12 common components found on PCBs, demystifying their roles and significance.
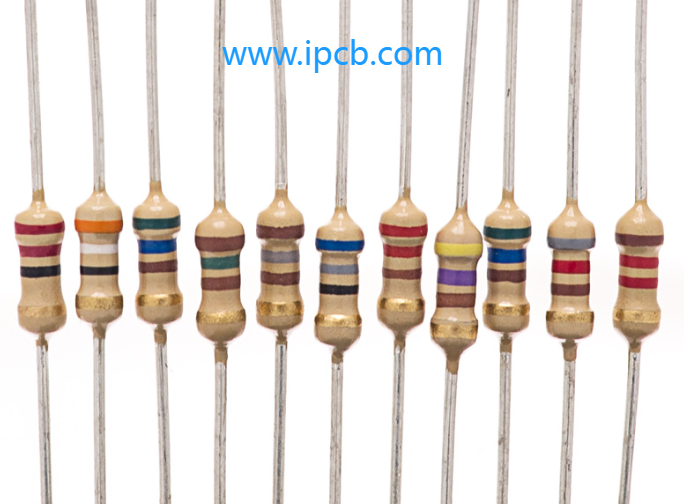
1. Resistors
Resistors are essential for regulating the flow of electric current in circuits. They come in various types such as carbon composition, metal film, and wirewound, each with specific characteristics and applications. By decoding color bands, you can determine a resistor’s resistance value, crucial for controlling voltage levels and protecting sensitive components.

2. Capacitors
Capacitors store and release electrical energy, consisting of two conductive plates separated by an insulating dielectric. They smooth out voltage fluctuations in power supply circuits and find applications in timing circuits, filtering circuits, and audio systems. Factors like capacitance value, voltage rating, and temperature stability influence capacitor selection.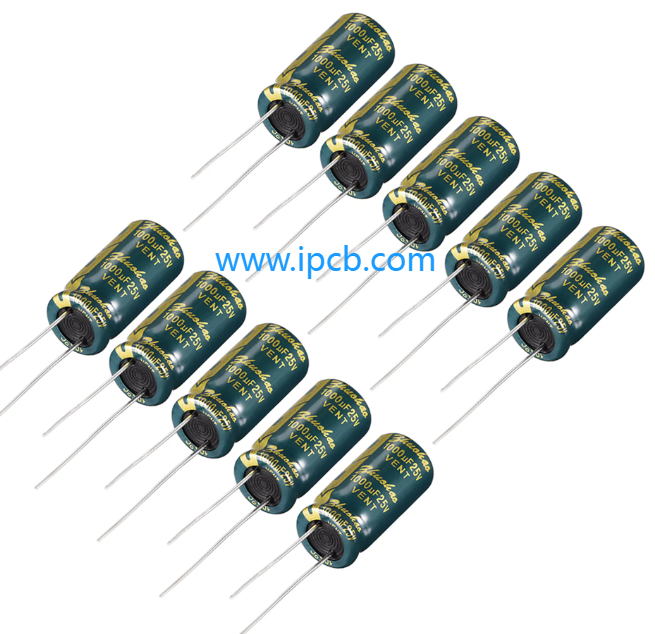
3. Inductors
Inductors store energy in the form of a magnetic field, playing roles in power supplies, RF circuits, and motors. They resist changes in current flow due to their inductance property, controlling speed and torque in motors and finding applications in wireless charging systems and transformers.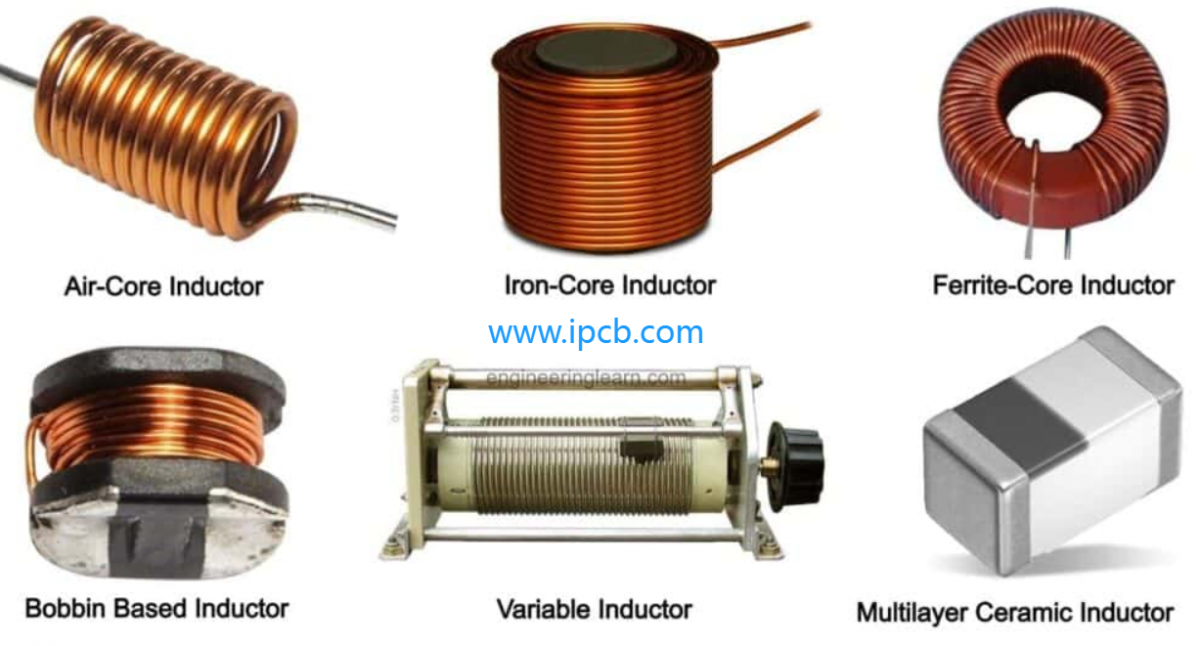
4. Potentiometers
Potentiometers, or pots, are variable resistors used for controlling electric current flow. They adjust volume, balance, and tone in audio equipment, control brightness in lighting systems, and serve in industrial settings for position sensing and control.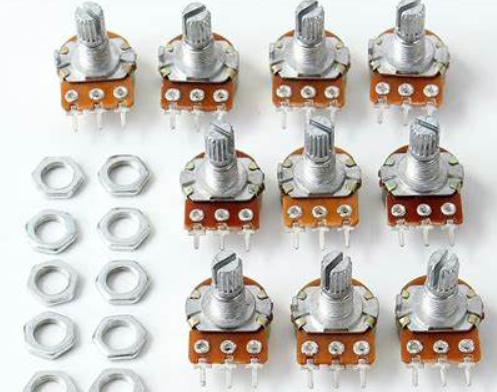
5. Transformers
Transformers transfer electrical energy between circuits by boosting or reducing voltage. They find applications in power distribution, instrumentation, audio equipment, and isolation for safety and noise reduction.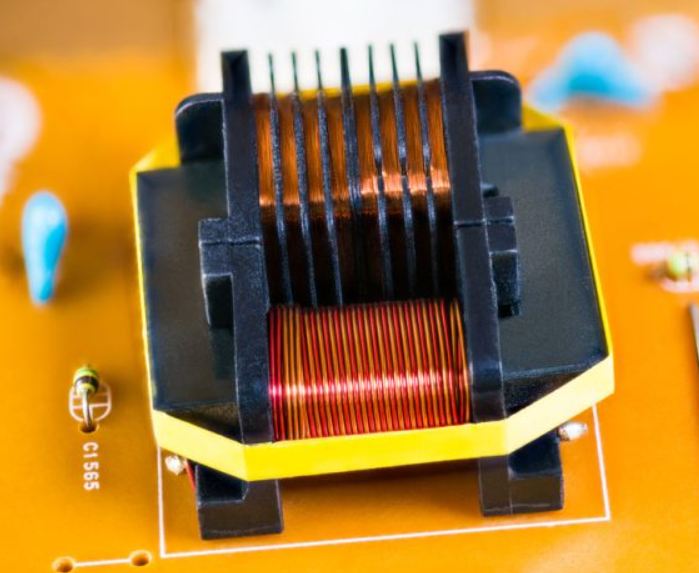
6. Diodes
Diodes allow current flow in one direction while blocking it in the other. They come in various types such as rectifier diodes, Zener diodes, LEDs, and Schottky diodes, each serving specific purposes in electronic circuits.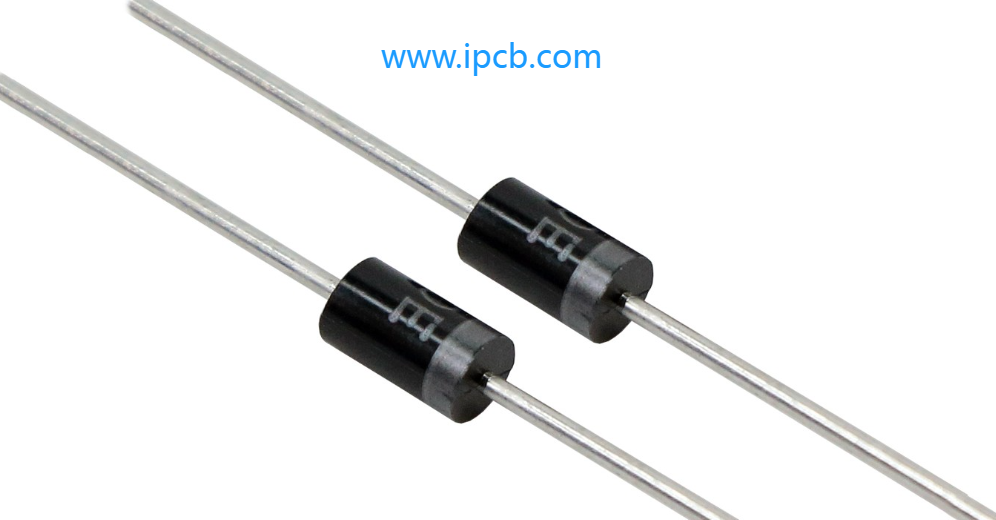
7. Transistors
Transistors amplify or switch electronic signals and power, crucial for compact, high-performance electronics. BJTs and FETs are common types used in amplifiers, switches, digital circuits, and integrated circuits.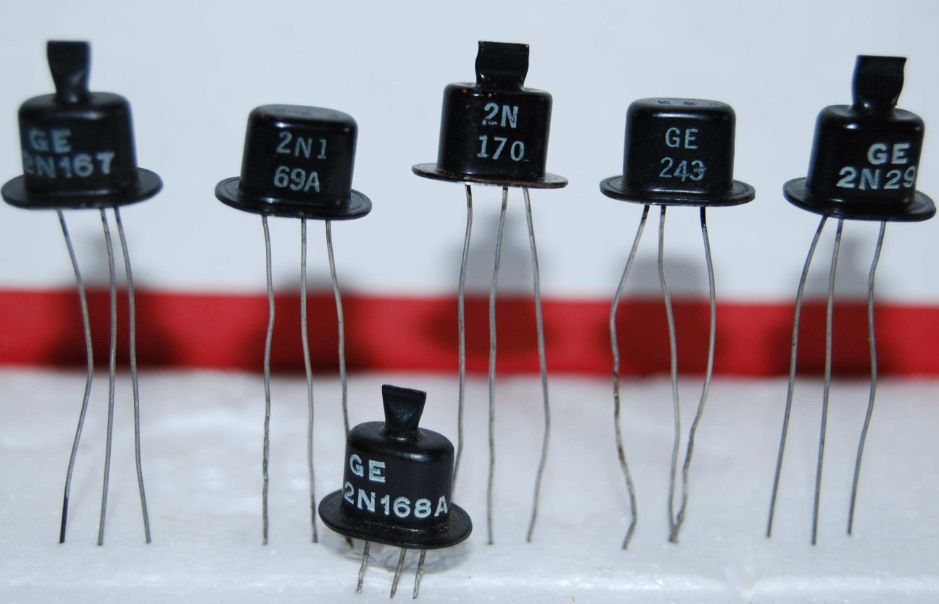
8. Silicon-Controlled Rectifier (SCR)
SCRs, or thyristors, control current flow in one direction, making them versatile for power control applications like dimmer switches, motor speed control, and voltage regulation.
9. Integrated Circuits (ICs)
ICs pack multiple electronic components onto a small silicon wafer, enabling faster processing speeds, increased functionality, and reduced power consumption. They power smartphones, medical devices, automotive systems, and more.
10. Crystal Oscillators
Crystal oscillators generate precise frequencies using crystal vibrations, crucial for timekeeping in watches, clocks, and GPS systems. Types include simple, TCXO, and VCXO oscillators, each offering specific advantages.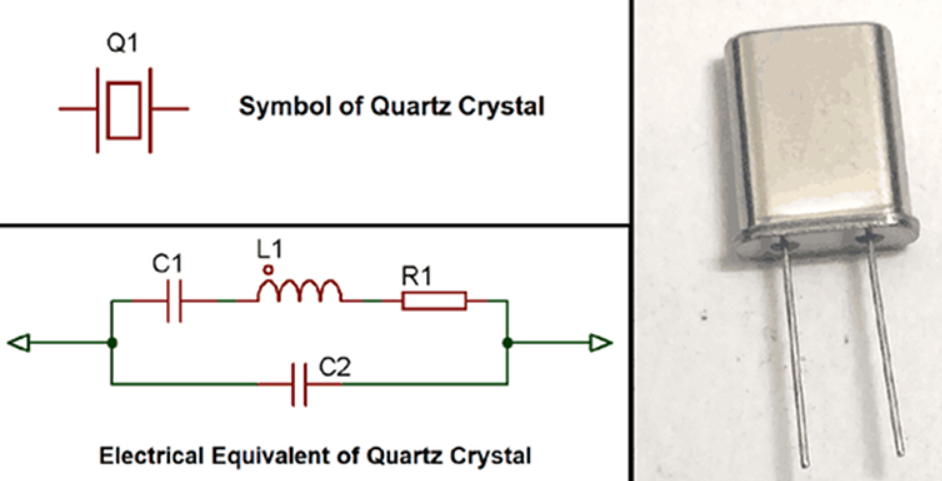
11. Switches and Relays
Switches control the flow of electric current in circuits, while relays use electromagnets to control larger currents remotely. They’re essential for device operation, offering various types like toggle switches, push-button switches, and electromagnetic relays.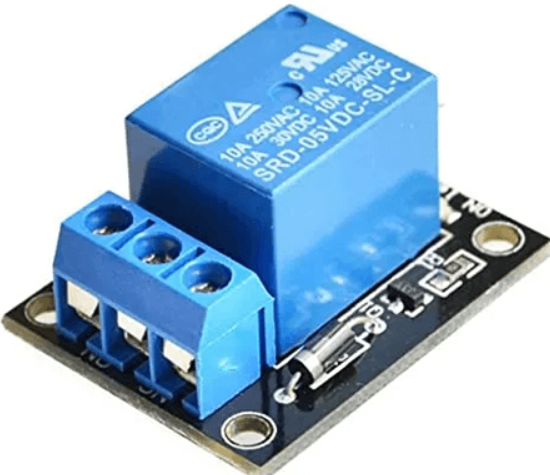
12. Sensors
Sensors detect and react to inputs from the physical environment, providing valuable data for monitoring and control. Types include proximity sensors, temperature sensors, motion sensors, pressure sensors, and light sensors, each serving specific applications.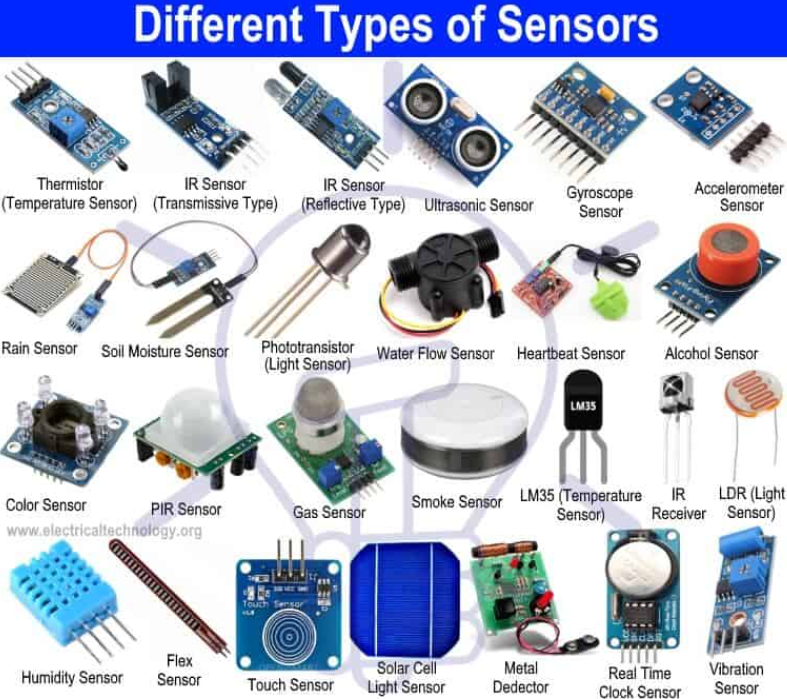
Conclusion:
In conclusion, this article has provided a comprehensive overview of 12 commonly used components on printed circuit boards (PCBs) for beginners. Exploring the role and significance of each component in electronic circuits, ranging from resistors and capacitors to more complex elements like integrated circuits and crystal oscillators. The discussion covered the fundamental characteristics and functions of these components, shedding light on their importance in the realm of PCB design and electronics.
By delving into the intricacies of components such as sensors, switches, and relays, are parts of a pcb the article aimed to equip beginners with a foundational understanding of the diverse elements that make up a circuit board components. The emphasis on identification and the role of each component contributes to the reader’s ability to navigate and comprehend electronic circuits effectively. As electronic devices continue to evolve, ic board components, a solid understanding of these components becomes increasingly crucial for enthusiasts, hobbyists, and professionals alike. This article, with its comprehensive coverage and emphasis on clarity, aims to empower beginners in their journey to grasp the essentials of circuit board parts design and electronic systems.
