- 05
- Oct
Explain the Flying Test of circuit board in detail
Explain the Flying Test of circuit board in detail

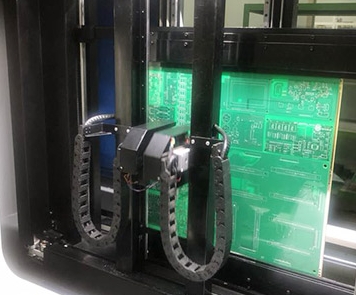
The principle of circuit board flying pin test is very simple. It only needs two probes to move x, y and Z to test the two ends of each circuit one by one, so there is no need to make another expensive fixture. However, due to the endpoint test, the measurement speed is very slow, about 10 ~ 40 points / sec, so it is more suitable for samples and small mass production; In terms of test density, flying needle test can be applied to very high density boards, such as MCM.
Principle of flying needle tester: it is to use four probes to conduct high-voltage insulation and low resistance conduction test (test the open circuit and short circuit of the line) for the circuit board, as long as the test document is composed of the customer’s original and our engineering draft.
After the test, there are four reasons for short circuit and open circuit:
1. Customer file: the tester can only compare, not analyze
2. Production line production: warpage, solder resistance and non-standard characters of PCB board
3. Process data conversion: our company adopts the engineering draft test, and some data (via) of the engineering draft is omitted
4. Equipment factors: software and hardware problems
When we received the board that passed our test and pasted it, we encountered the through-hole blockage. I don’t know what caused it. We mistakenly thought it was our test, but it was also shipped. In fact, there are many reasons for the through-hole blockage.
There are four reasons for this:
1. Defects caused by drilling: the plate is made of epoxy resin glass fiber. After drilling, there is residual dust in the hole, which is not cleaned, and copper cannot be deposited after curing. Generally, we will test it in the flying needle test link.
2. Defects caused by copper deposition: the copper deposition time is too short, the hole copper is not full, and the hole copper is not full when tin is applied, resulting in poor conditions. (in chemical copper deposition, there is a problem in one link of glue slag removal, alkaline oil removal, micro etching, activation, acceleration and copper deposition, endless development, excessive etching, and the residual solution in the hole is not washed clean. Specific links are analyzed in detail)
3. Circuit board vias require too much current and are not informed in advance of the need to thicken the hole copper. This problem often occurs when the current is too large to melt the hole copper after power on. The current of the theoretical value is not proportional to the actual current, resulting in the direct melting of the hole copper after power on, resulting in the non continuity of the via, which is mistakenly thought that the test was not carried out.
4. Defects caused by the quality and technology of SMT tin: the long residence time in the tin furnace during welding leads to the melting of hole copper, which leads to defects. Novice partners are not very accurate in judging the material in terms of control time, and make mistakes under the material at high temperature, which leads to the failure of hole copper melting. The current plate factory can basically do the flying needle test on the samples, so if the plate making is still to find 100% flying needle test to avoid problems found in the hands of the plate.
Conclusion: through learning, we will know more about the small details of flying needle test and know where to go in our work.
